Plate Tectonics Theory
Plate tectonics is a theory. That means it has not been proven, but no evidence exists to disprove it. Several lines of reasoning or "proofs" have been used as evidence to support the theory. They include:
- Shape of the continents
- Paleomagnetism
- Age of Rocks
- Climatology
- Identical rock units
- Identical topographic units
- Fossil evidence
Click on each of the topics above to read an explanation.
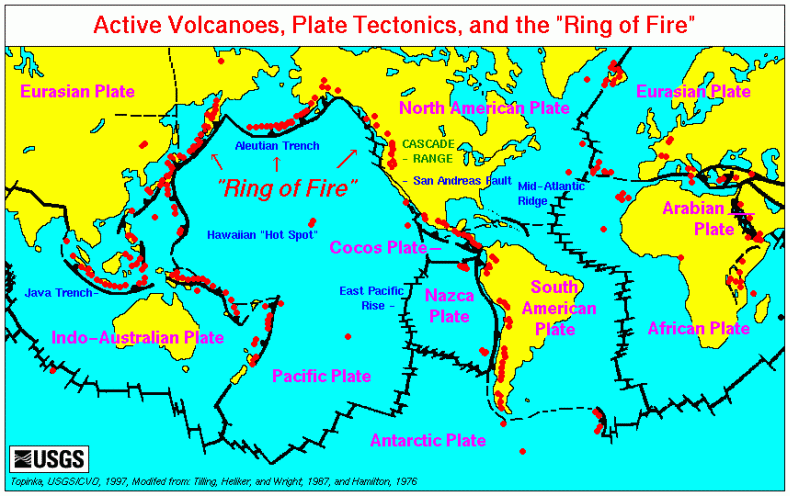
The Theory of Plate Tectonics provided a model for geology on the Earth. It explained why volcanoes and earthquakes occurred in certain areas of the Earth (along plate boundaries) while other regions were quiet geologically.
This theory helped geologists realize that some areas that seemed geologically quiet such as
Mount Rainier
and other Cascade volcanoes were merely dormant not extinct. The theory let geologists make long-term geologic predictions and calculate the probability of geologic events such as an earthquake on the San Andreas Fault (90% probability within the next 50 years). The Theory of Plate Tectonics gave geologists a deeper understanding of the geologic activity found on Earth.
Continue on to "Plate Movements and Plate Boundaries"